Introduction
If you are looking to invest in the US stock market, the first step is learning how to open a Brokerage Account in the US. Unlike traditional investing, where shares were once held as physical certificates, modern investing in America is completely digital. A Brokerage account holds your securities electronically, which allows you to buy and sell those securities online.
Having gone through this process myself as an international investor living in the US, I can confidently say that the journey may look intimidating at first, but with the right brokerage and an understanding of compliance requirements, it is straightforward. In this detailed guide, I will walk you through everything you need to know, from account requirements and the application process to taxation, brokerage fees, and practical case studies for different investor types.
By the end of this blog, you will have a step by step understanding of how to open a Brokerage Account in the US in 2025 and what to expect as an investor.
What is a Brokerage Account in the US
A brokerage account is an investment account that allows you to buy, sell, and hold securities such as stocks, ETFs, bonds, and mutual funds in electronic format. It acts as your gateway to the financial markets, ensuring safety, ease of transfer, and convenience when managing investments. Before you open a brokerage account, it’s important to understand how the stock market works. If you’re new to investing, check out our detailed guide on what the stock market is?
In the US a brokerage account combines both the storage and transaction functions into a single platform. This means that when you open an account with popular brokers like Fidelity, Charles Schwab, E*TRADE, or Robinhood, you can directly deposit money, trade securities, and hold your investments in one place.
Why You Need a Brokerage Account in the US
Here are some of the key reasons why investors in the US rely on these accounts:
- Safety and Security: Your investments are stored electronically, eliminating risks of physical loss or theft.
- Convenience: Buy or sell securities in real time with just a few clicks.
- Global Access: Many US brokers also allow access to international markets.
- Integration: Accounts are linked with your bank and tax profile, simplifying compliance.
- Transparency: Statements and trade history are available instantly online.
Whether you are a resident American, a green card holder, or even a foreign investor with US market access, you cannot invest in US equities without a Brokerage account.
Step by Step Guide: How to Open a Brokerage Account in the US
Opening a brokerage account in the US involves a few steps. While every broker has its own process, the general workflow is almost identical.
Step 1: Choose a Reputable Broker
Some of the leading US brokers include:
When choosing a broker, look for:
- Commission fees
- Account minimums
- Platform usability
- Research tools and education
- Customer support
- Access to international markets
Step 2: Gather Your Documents
You will typically need:
- Social Security Number (SSN) or Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
- Government issued photo ID (Passport or Driver’s License)
- Bank account details (for funding and withdrawals)
- Employment and financial information (for compliance with SEC and FINRA)
Step 3: Submit Your Application
Most brokers allow you to apply online. The application form will require your personal details, tax information, and investment objectives.
Step 4: Account Verification
Brokers conduct a KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti Money Laundering) check. Verification may take a few hours to a few days depending on the broker.
Step 5: Fund Your Account
You can transfer funds through:
- ACH (Automated Clearing House) transfer from your bank
- Wire transfer
- Check deposit
- Linking your payroll account in some cases
Step 6: Start Trading
Once your account is funded, you can begin buying and selling securities directly from your broker’s app or website.
Brokerage Fees and Charges in the US
One of the most important factors in selecting a broker is the fee structure. In 2025, most US brokers have adopted zero commission trading for stocks and ETFs, but fees still exist in certain areas.
Typical Brokerage Charges
- Stocks and ETFs: $0 commission (Schwab, Fidelity, Robinhood, etc.)
- Options Trading: $0 commission + $0.65 per contract
- Mutual Funds: Vary; some are free while others may have transaction fees
- Margin Accounts: Interest rates ranging between 5% to 12% depending on the broker
- Wire Transfers: $20 to $30 per transaction
- Account Maintenance Fees: Usually waived, though some legacy brokers still charge
When comparing brokerage charges, always check the fine print. For example, while Robinhood offers free trading, advanced investors may find Fidelity or Schwab more cost effective because of superior research tools and lower margin rates.
Taxation Rules for Investors in the US
If you are opening a Brokerage account in the US, taxation is a critical aspect to understand. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires you to report all investment income.
Key Tax Elements
- Capital Gains Tax
- Short term (held less than 12 months): Taxed as ordinary income (10% to 37%).
- Long term (held over 12 months): 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on income bracket.
- Dividend Tax
- Qualified dividends: Lower tax rates (0%, 15%, or 20%).
- Non qualified dividends: Taxed as ordinary income.
- Reporting Requirements
- Brokers issue a Form 1099 to investors summarizing dividends, gains, and interest.
- You must include this in your annual tax filing.
- Foreign Investors
- If you are a non resident investing in the US, a 30% withholding tax applies on dividends (may be reduced by tax treaties).
For detailed tax guidelines, refer to the IRS investment income rules.
Case Study 1: First Time Investor in the US
Profile: Emily, age 28, software engineer in California.
Emily wanted to begin investing in 2025 with a focus on ETFs. She compared Robinhood and Fidelity. While Robinhood offered a sleek app, she chose Fidelity because of its fractional share investing, superior research tools, and access to retirement accounts.
- Initial Investment: $5,000 in ETFs
- Annual Fees Paid: $0 commissions
- Tax Consideration: Capital gains deferred until selling
Emily found the process simple: online signup took 20 minutes, her account was approved in 2 days, and she began investing immediately after funding via ACH transfer.
Advanced Taxation and Investment Planning
While basic taxation covers capital gains and dividends, serious investors in the US need to look deeper into tax optimization strategies.
1. Tax Loss Harvesting
If you sell securities at a loss, you can use those losses to offset capital gains. For example:
- Gain on Stock A: $5,000
- Loss on Stock B: $3,000
- Net taxable gain = $2,000
Many brokers (like Fidelity and Schwab) provide automated tax loss harvesting through their robo-advisory platforms.
2. Retirement Accounts (IRA and 401k)
Opening an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) or contributing to a 401(k) allows you to invest with tax advantages:
- Traditional IRA/401k: Contributions are tax deductible; withdrawals taxed later.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are after tax; withdrawals are tax free.
This is why many US residents prefer starting their investment journey with a retirement account before opening a standard brokerage account.
3. International Tax Considerations
Foreign investors opening a US brokerage account must file Form W-8BEN to claim reduced tax rates on dividends under tax treaties. For example, investors from India may benefit from a lower withholding tax rate than the standard 30%.
4. Estate and Inheritance Taxes
For high net worth investors, the estate tax may apply if assets exceed $13.61 million (2024 limit, indexed annually). Structuring investments via trusts and retirement accounts can help in estate planning.
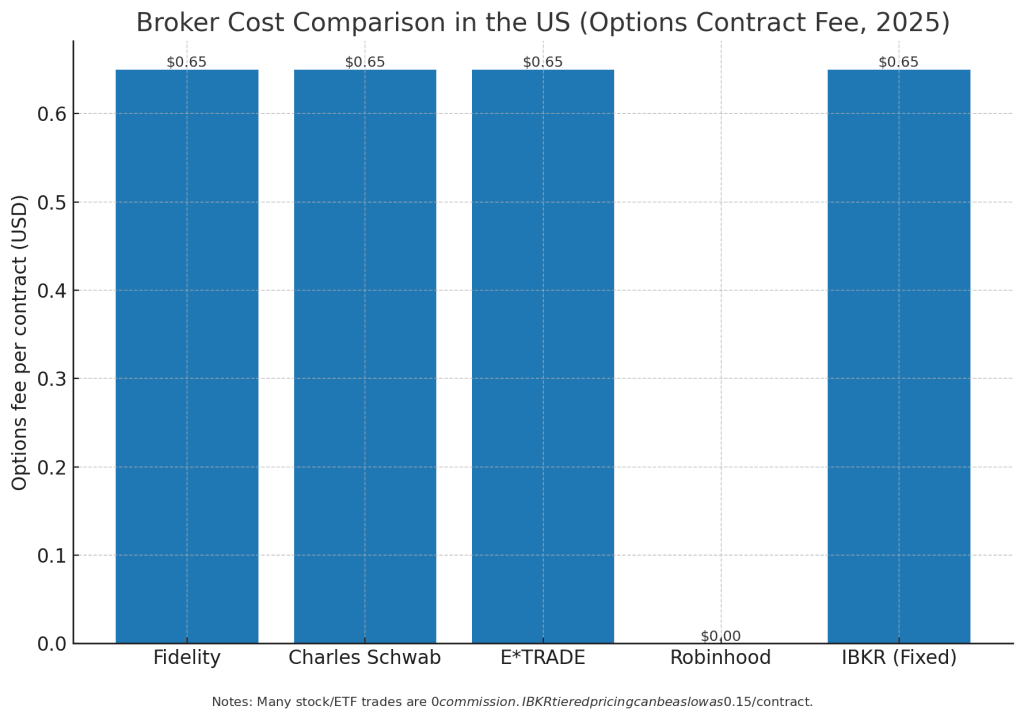
Broker Comparison in the US (2025)
Choosing the right broker can make a huge difference in your investing journey. Here’s a comparison of some of the top US brokerage firms:
| Broker | Commission (Stocks/ETFs) | Options Fee | Margin Rate (approx.) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charles Schwab | $0 | $0.65/contract | ~6% | Long term investors, retirement accounts |
| Fidelity | $0 | $0.65/contract | ~5% | Fractional shares, research tools |
| E*TRADE | $0 | $0.65/contract | ~7% | Active traders, options |
| Robinhood | $0 | $0.00–0.65 | ~11% | Beginners, app based investors |
| Interactive Brokers (IBKR) | $0 | $0.65/contract | ~5.5% | Global investors, professionals |
Key takeaway: If you’re a beginner, Robinhood may look attractive, but Fidelity and Schwab provide stronger long term benefits. For international or advanced traders, Interactive Brokers is unmatched.
Case Study 2: Retiree Investor
Profile: John, 62, recently retired in Texas.
John had $250,000 in retirement savings and wanted low risk investments. He opened a Charles Schwab account because of its extensive retirement planning services.
- Investment Choice: Mix of dividend ETFs and municipal bonds
- Brokerage Fees: $0 commissions, minimal fund costs
- Tax Advantage: Some municipal bonds exempt from federal taxes
- Outcome: Stable monthly income stream with reduced tax liability
Case Study 3: Active Day Trader
Profile: Mark, 35, active trader in New York.
Mark required fast execution, margin trading, and advanced analytics. He compared TD Ameritrade and Interactive Brokers. He finally chose Interactive Brokers (IBKR).
- Initial Capital: $50,000
- Trading Style: Options and futures
- Brokerage Cost: ~ $0.65 per options contract, competitive margin rates
- Outcome: Access to international markets and professional level tools
Case Study 4: International Investor
Profile: Priya, 40, Indian citizen investing in the US market.
Priya wanted exposure to US technology stocks like Apple, Google, and Tesla. She opened an Interactive Brokers global account from India.
- Documentation Required: Passport, Indian PAN card, proof of address
- Taxation: W-8BEN form submitted → Withholding tax on dividends reduced from 30% to 25% under India-US treaty
- Brokerage: $0 commission on stocks, low FX conversion fees
- Outcome: Seamless access to US equities without relocating
Security and Compliance Considerations
When opening a Brokerage account in the US, it’s important to ensure your funds are secure and your broker is regulated.
Regulatory Bodies in the US
- SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission): Oversees the securities markets
- FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority): Regulates brokers and trading practices
- SIPC (Securities Investor Protection Corporation): Provides up to $500,000 protection for investors if a brokerage fails
Safety Tips for Investors
- Always verify your broker is SEC and FINRA registered.
- Avoid unknown apps promising “guaranteed returns.”
- Use two factor authentication (2FA) on your trading account.
- Regularly download and reconcile your brokerage statements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Opening a Brokerage Account
- Ignoring Fees Beyond Commissions – Many new investors only check for $0 commissions but ignore margin rates, inactivity fees, and withdrawal charges.
- Not Understanding Tax Rules – Failing to report dividends or capital gains can attract IRS penalties.
- Choosing the Wrong Broker – Beginners may choose a platform that looks easy but lacks tools for growth.
- Overleveraging with Margin – Trading with borrowed money is risky and should only be used by experienced traders.
- Skipping Research – Blindly investing in “hot stocks” without due diligence can wipe out capital quickly.
Checklist Before Opening Your Account
Here’s a quick ready to use checklist:
- Compare at least 2 to 3 brokers
- Gather necessary KYC documents (SSN, ID, bank info)
- Understand brokerage charges (commissions, margin, maintenance)
- Learn about US taxation (capital gains, dividends, W-8BEN for foreigners)
- Check security (SIPC protection, 2FA)
- Define your investment goals (retirement, trading, global exposure)
Conclusion
Opening a Brokerage Account in the US in 2025 is simpler than ever, thanks to digital onboarding and zero commission structures. Whether you are a beginner starting with $500, a retiree seeking stable income, or an international investor looking for global diversification, the US brokerage ecosystem provides solutions for everyone.
The most important steps are:
- Choose the right broker.
- Understand taxation.
- Plan your investments according to your goals.
- Prioritize safety and compliance.
With the right planning and a reliable brokerage partner, you can confidently participate in the US stock market and build long term wealth.